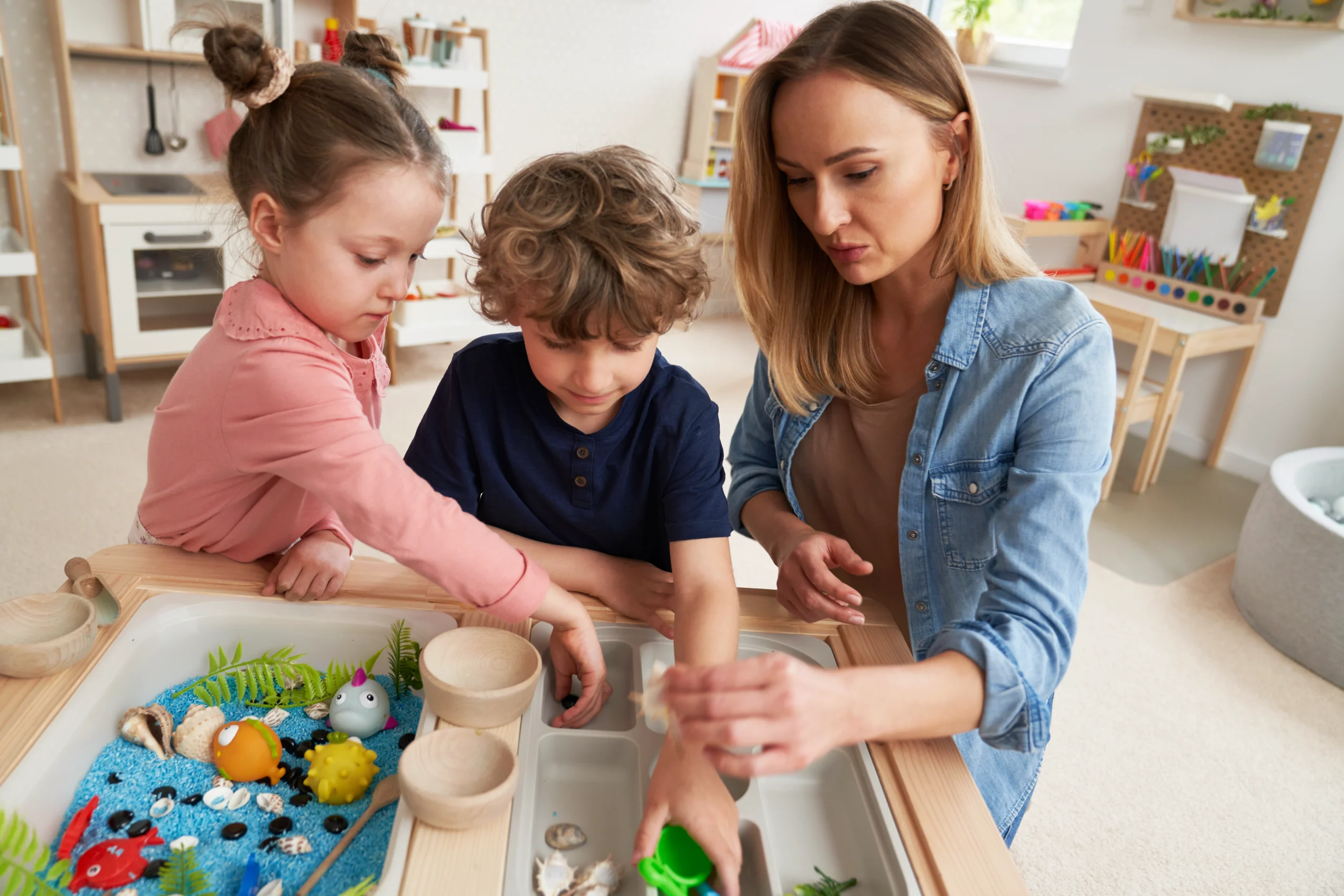
The human brain is interrelated and therefore in early childhood. Every look, every word, every touch on part of a parent establishes the neural patterns of emotional intelligence and trust. Neuroscience has proven that the regular affectionate availability can even physically change the brain of a child to respond to stress, safety and relationships. This makes attachment not only an emotional concept, but a biological concept that lies in the core of the Holistic Child Development.
Knowledge of Attachment With Neuroscience.
The emotional linkage that forms between the child and its parent is referred to as attachment and arises as an outcome of day to day attention and empathy. When a child is calm, secure, and open, then the brain will generate serotonin and oxytocin which are the chemicals linked to serenity and joy.
It is a supportive family environment that ensures that the limbic system which is the emotional and balancing of the child develops in stability and not in fear. Conversely, the unpredictable care activates processes of stress, which the brain learns to be awake rather than being in a relaxed state. This is the reason the presence in daily life is more important than each of the parenting acts.
Children and EI: The Reason to Be Emotionally Intelligent.
The process through which a child develops emotional intelligence in child development begins when the children see how their caregivers are handling emotions. Parents also display the skill to name and manage emotions by not responding reactively to their children.

The more the parent thinks as the child does and ascertains it, the more are the neural pathways strengthened in the sphere of caring and self-awareness. This is a resilience formation of these minor and repetitive experiences. Emotional learning cannot be taught in the lessons, but experiences of lived interactions is the opportunity to receive and understand feelings.
Empathy, Respect and Compassion in Parenting.
Respectful parenting and Empathy and Compassion Parenting focus on the interpretation of the feeling that a child acts in the manner and do not punish them immediately. This will help the child to feel instead of being judged.
- Recently without interruption.
- Validate before advising.
- Boundaries must be appreciated and not dictated upon.
Individual parents who act in a manner that makes use of empathy inculcate the same to kids. This helps in building empathy and compassion in young children resulting in creating emotional stability and greater sensitivity to the society.
Difficult Times of Parenting Unconditional Love.
True growth is made in difficult circumstances. Unconditional Love Parenting means that you have to be emotional even when you are frustrated with the child. This is what neuroscience demonstrates and helps in managing the amygdala of the child, which is the centre of the brain of fear, so that the child becomes less fearful and more trusting.
The Practicing unconditional love in challenging parenting situations can include the unconditional love shown by the parents in the challenging situations of parenting by:
- Delaying before responding.
- Using a low tone voice and posture.
- Post conflict reassurances.
This type of behaviour informs the brain of the child: love is not withheld in a time of stress. This, with time, reinstates emotional memory which is a lesson in security and not fear.
Family Relationship and Day to Day Companionship.
Small repetitive gestures of existence are beyond perfection. Activity in a group like meals, reading or a weekly Family Meeting helps children develop association of being attached with being safe. It is the mirror neurons of the brain that are involved in these instances and that the parent-child emotions are aligned.
Teamwork and knowledge is generated through this spirit of togetherness. The formation of long-term wellbeing is built at the level of families that make a conscious slowdown and devote time to each other that forms the neural conditions. Trust happens to be the design of presence.
Conclusion
Attachment is not an event it is the science of day-to-day connection. Parents not only influence the emotional level but the brain also organises itself with the help of empathy, respect, and Unconditional Love Parenting. The process of developing the child holistically involves minute gestures of consistent love in order to establish neural interconnections and emotional security. Having that, parents do not just create a child, they create that child brain to learn to love, to trust and prosper as well.
Visit Vedandi Brahambhatt on Instagram and YouTube to read daily posts, tips on mindful parenthood and professional advice on how to bring up an emotionally balanced child.
FAQs
What is the neuroscience behind attachment?
The trust and the emotional intelligence in child development of the early childhood is enhanced because the parts of the brain involved in safety and regulation are triggered by the attachments.
How does the presence affect the development process of a child?
Connexion also assists in the construction of neural networks that govern emotions and the level of stress and improves wellbeing over the long run.
What do we mean under respectful parenting?
It is an approach technique that entails compassion, communication, and comprehension in a bid to make children feel that they are treasured and secure.
How can children in families be empathised?
In order to express empathy, involve in collective activities, listen and encourage open communication during Family Meeting and family interaction.Is unconditional parenting love relevant?
Even during the conflict, stable love reforms the brain to enable it to adjust to the strength and trains children on the idea of being emotionally stable through Unconditional Love Parenting.